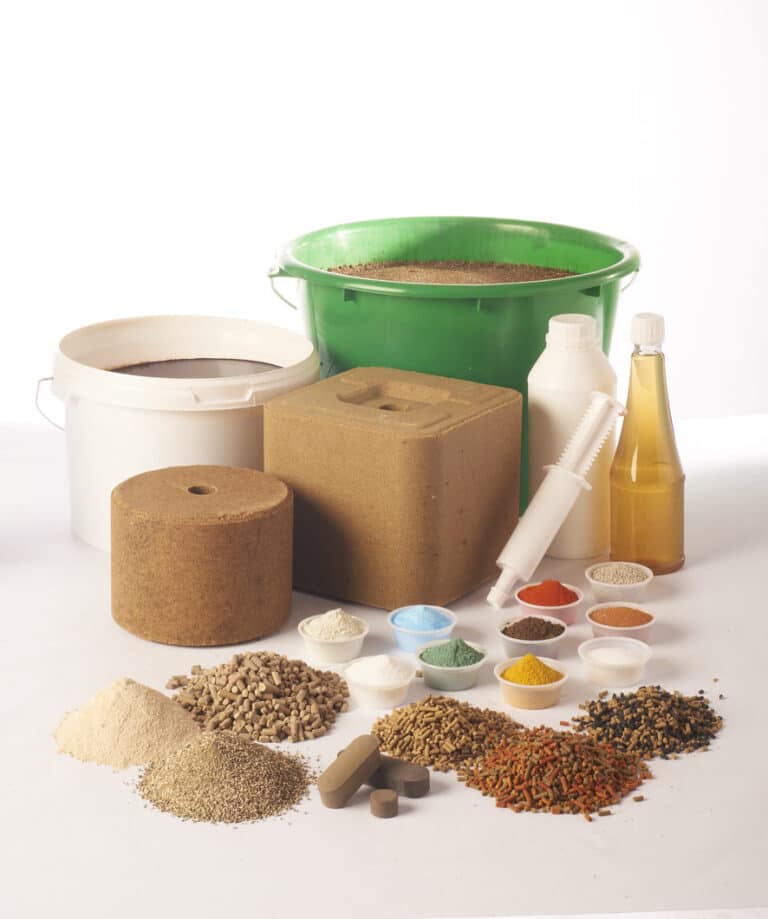
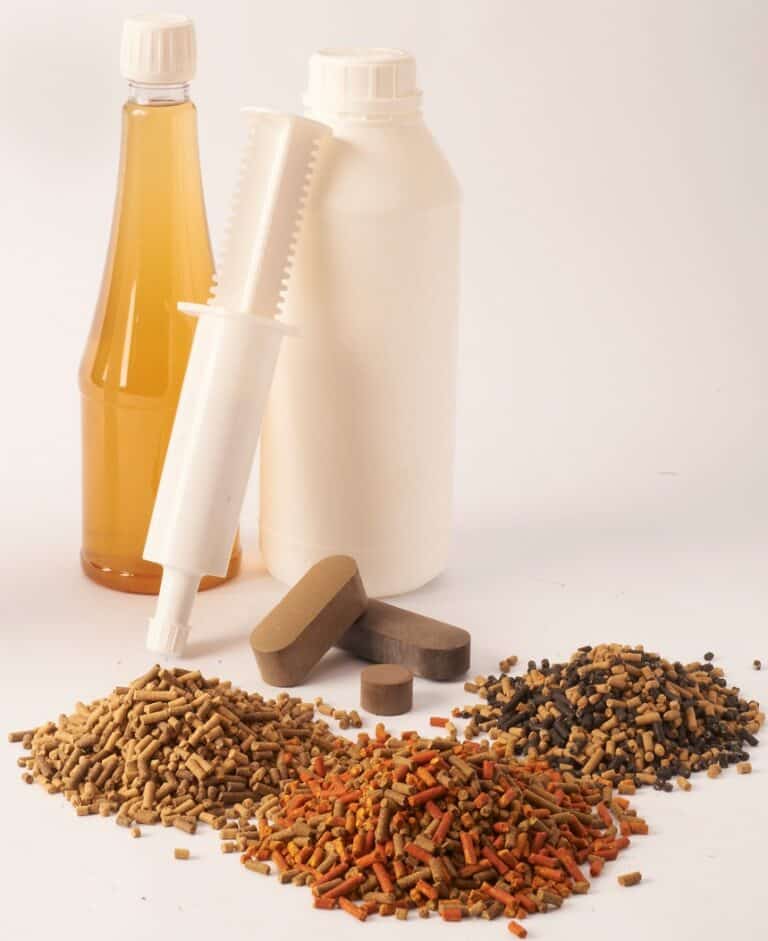
Some complementary feeds are specifically formulated to help animals during certain life phases. They are given to animals in order to prevent nutritional unbalances and meet specific needs that occur in different physiological phases, such as the growth of young animals, weaning, early or late production, changes in feed, reproduction… These phases may lead to deficiencies in vitamins and trace elements, stress, digestive disorders, reproduction problems, growth slowing… These complementay feeds carry claims that highlight the product’s interest and functionality. They are marketed with different presentations to best adapt to the working practices of farmers and to the living situations of the animals: powder, fine granular feed, pellets, licks, paste, gel, liquid, gradual-release bolus, individual tablet…
The scientific, technological and zootechnical expertise of AFCA-CIAL’s members ensures a continuous innovation to feed manufacturers and animal sectors by integrating societal expectations and environmental requirements.